Hi, Friends!
Welcome back, this blog will talk about Categories, Characteristics, and Advantages of Big Data.
'Big Data' is a term used to describe a collection of data that is huge in size and yet growing exponentially with time. In short, such a data is so large and complex that none of the traditional data management tools are able to store it or process it efficiently.
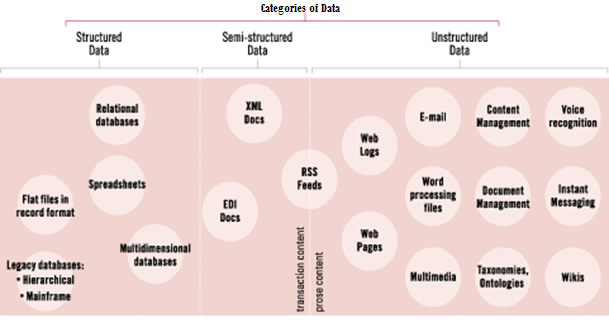
Categories of Big Data:
- Structured Data: Any data that can be stored, accessed and processed in the form of fixed format is termed as a 'structured' data. For Example, table in a database.
- Semi-Structured Data: Semi-structured data can contain both the forms of data. We can see semi-structured data as a structured in form but it is actually not defined with e.g. a table definition in relational DBMS. Example of semi-structured data is a data represented in an XML file, likes or reactions on Social Media, Log files of any web portal.
- Unstructured Data: Any data with unknown form or the structure is classified as unstructured data. In addition to the size being huge, unstructured data poses multiple challenges in terms of its processing for deriving value out of it. A typical example of unstructured data is a heterogeneous data source containing a combination of simple text files, images, videos etc.
Characteristics of Big Data:
- Volume: Business’ collect data from a variety of sources, including social media, business transactions, and information from sensor or machine-to-machine data. In the past, storing it would’ve been a problem – but new technologies (such as Hadoop) have eased the burden.
- Velocity: Data streams in at an unprecedented speed and must be dealt with in a timely manner. RFID tags, sensors, and smart metering are driving the need to deal with torrents of data in near-real time. Managing data velocity is necessary as this data is fed for data analysis in many different algorithms of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.
- Variety: Data comes in all types of formats – from structured, numeric data in traditional databases to unstructured text documents, email, video, audio, stock ticker data and financial transactions.
- Veracity refers to the messiness or trustworthiness of the data. With many forms of big data, quality and accuracy are less controllable (just think of Twitter posts with hash tags) but big data and analytics technology now allow us to work with these type of data. The volumes often make up for the lack of quality or accuracy.
- Value: Then there is another V to take into account when looking at Big Data: Value! It is all well and good having access to big data but unless we can turn it into value it is useless. So you can safely argue that ‘value’ is the most important V of Big Data. It is important that businesses make a business case for any attempt to collect and leverage big data.
Advantages of Big Data Processing:
- Ability to identify the root causes of failures and issues in real time,
- Fully understanding the potential of data-driven marketing,
- Generating customer offers based on their buying habits,
- Revaluating risk portfolios quickly,
- Personalizing the customers experience, and
- Adding value to online and offline customer interactions.
Happy Learning!

Comments
Post a Comment