In the prior
versions of SQL Server releases Microsoft has focused on Azure features, in
contrast to it in SQL Server 2016 Microsoft has focused on moving to a common
code based platform for standalone SQL Server and Azure SQL Database which will
allow developers to adopt new features easily. Following are the new features
to meet your needs of the rapid developing industry:
- Improved Performance:
o
Query Store: Common problem faced by the developer while
upgrading to the latest version of SQL Server is there is a huge impact on the
performance of the query optimizer, here’s a solution to the problem. The Query
store helps you on query plan choice and performance, it automatically captures
history. You can configure query store at database level using ALTER DATABASE SET command.
o
Real time operational analytics*: Generally, businesses have separate
systems for operational (OLTP) and analytics workload. For example, a bank
deals with multiple transactions offline as well as online in a day, so any
downtime or slowdown will directly impact the business’s bottom line.
Therefore, to maintain the performance and availability separate systems are
maintained, which in turn is an added cost to the business. The solution to
this problem is Real time operational analytics with in-memory technology in
SQL Server 2016. It enables running analytics queries directly on your
operational workload using columnstore indexes on a rowstore table.
- Improved Security:
o
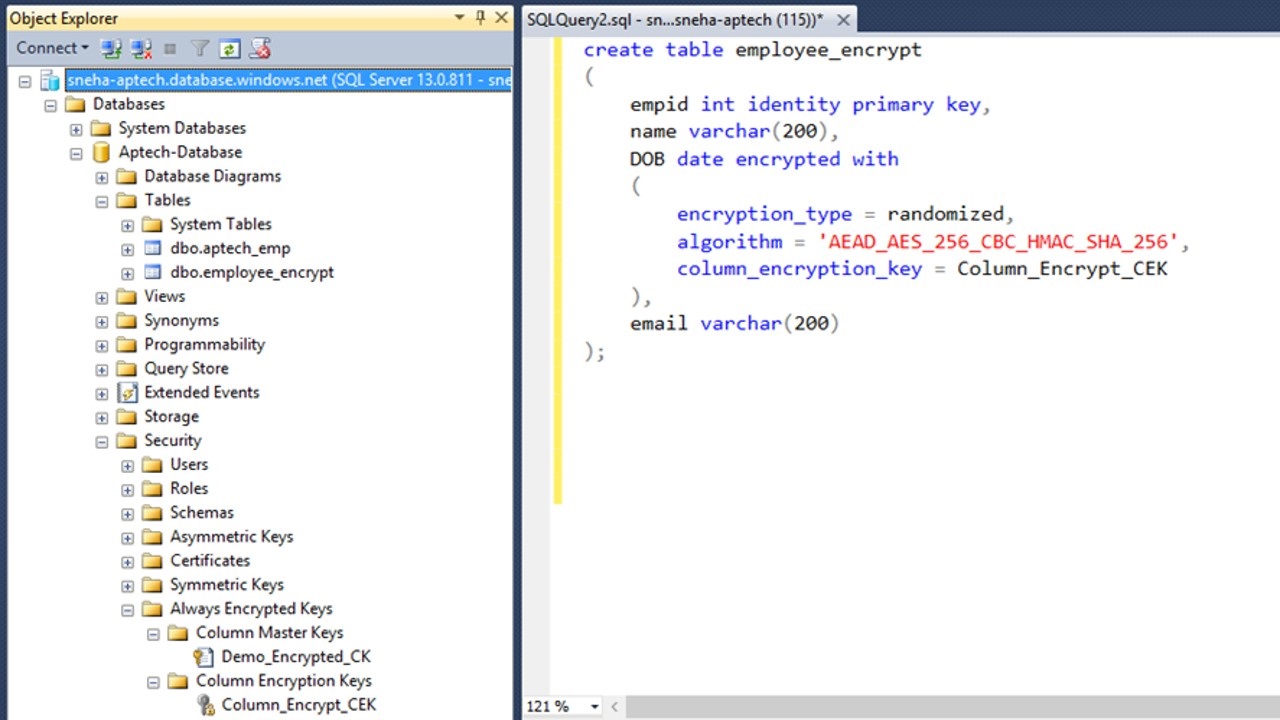
Always encrypted*: We hear about major data breach in
different companies every month, the solution to the problem is the encrypting
feature of SQL Server 2016. Always Encrypted enables client application
owners to control who gets access to see their applications confidential data.
This is possible with ENCRYPTED WITH command during the creation of the table.
o
Row-level Security: A feature that other databases have had
for many years, and SQL Server has lacked natively is the ability to provide
row-level security (RLS). This restricts which users can view what data in a
table, based on a function. SQL Server 2016 introduces this feature, which
is very useful in multi-tenant environments where you may want to limit data
access. This can be achieved using CREATE SECURITY POLICY command.
o
Dynamic data masking: A way to implement abstraction in
database is dynamic data masking. Where the owner can decide who can view which
data, in order to protect the confidential information.
- Fresh introduction to Programmability:
o
JSON Support: With SQL Server 2016 you can now
interchange JSON (Java Script Object Notation) data between applications and
the SQL Server database engine. By adding this support Microsoft has
provided SQL Server the ability to parse JSON formatted data so it can be
stored in a relation format.
o
PolyBase queries over Hadoop data*: PolyBase technology simplifies
relational & non-relational data management by enabling users to access
data from Hadoop with the help of T-SQL Queries. This feature will benefit you
if your regular data processing involves dealing with a lot of large text files
-- they can be stored in Azure Blob Storage or Hadoop, and queried as if they
were database tables.
o
Temporal Tables: This feature specifies that relational
databases should also support the ability to query the table from the point of
view of any point in time. Basically, it means that database should enable
system-versioning and while doing so, we create a history of the source table
to another table called temporary table.
- Enhancement in Cloud-readiness:
o
SQL Server Stretch Database: One of the common problem in all the
companies is getting the cheap memory for expansion for storage. Solution to
this problem is Stretch Database, which means you can stretch/expand your
on-premise or stand-alone database to SQL Azure database on cloud. The basics
of Stretch Database are that some part of your tables (configurable or
automated) will be moved into an Azure SQL Database in the cloud in a secure
fashion. When you query those tables, the query optimizer knows which rows are
on your server and which rows are in Azure, and divides the workload
accordingly.
Few enhancements in the older features:
- In-Memory OLTP*: also known as ‘Hekaton’ and ‘In-Memory Optimization’ was introduced in SQL Server 2014 majorly used to optimize Online Transaction Processing(OLTP). Its main features are Memory-Optimized tables and Natively-compiled Store procedures (can be achieved by using the specific syntax while creating the objects). Memory-Optimized tables eliminates locks & latches, the data reading and writing happens to the memory directly which gives performance advantage. Native-compiled stored procedures access only memory-optimized objects and when compiled are converted to native code i.e. DLL. It is best utilized where there is huge work load i.e. capturing data of sensors in IoT, share market, online gaming platforms etc.
- Enhancement in T-SQL: Following new commands have been introduced in SQL Server 2016.
o
TRUNCATE
TABLE WITH PARTITIONS
o
DROP
IF EXISTS
o
ALTER
TABLE WTH (ONLINE = ON | OFF)
o
COMPRESS
and DECOMPRESS functions
o
FORMATMESSAGE
statement
Happy Learning!





Comments
Post a Comment